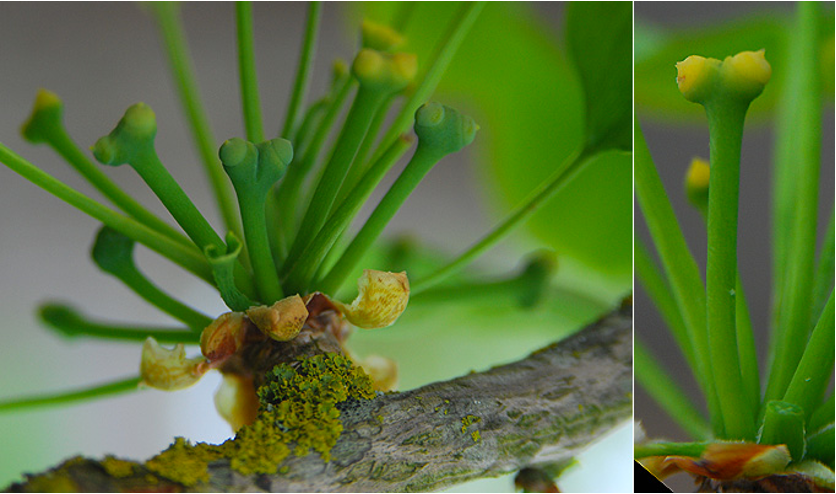
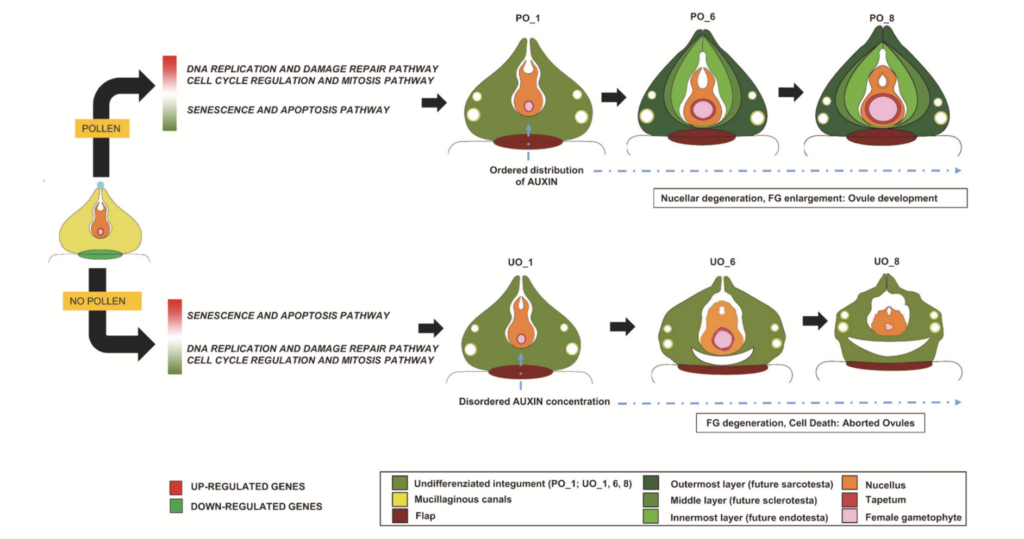
Development of pollinated and unpollinated ovules in Ginkgo biloba: unravelling the role of pollen in ovule tissue maturation
ABSTRACT In gymnosperms such as Ginkgo biloba, the arrival of pollen plays a key role in ovule development, before fertilization occurs. Accordingly, G. biloba female plants geographically isolated from male plants abort all their ovules after the pollination drop emission, which is the event that allows the ovule to capture pollen grains. To decipher the mechanism induced by …